
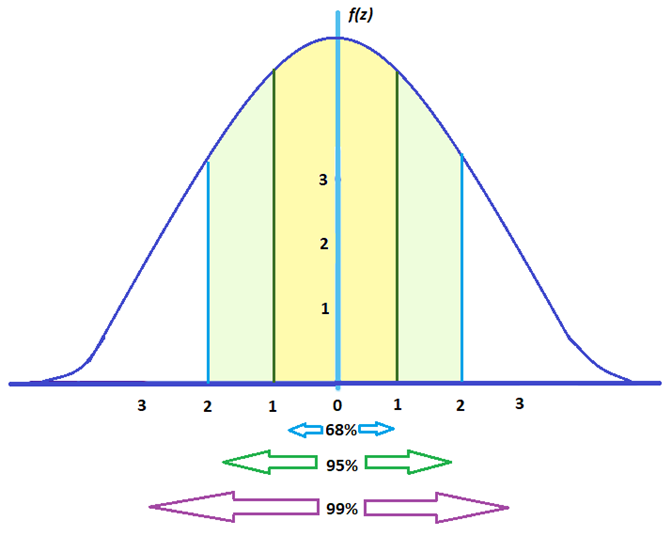
This means that to calculate the upper and lower bounds of the confidence interval, we can take the mean ☑.96 standard deviations from the mean. Example: Critical valueIn the TV-watching survey, there are more than 30 observations and the data follow an approximately normal distribution (bell curve), so we can use the z distribution for our test statistics.įor a two-tailed 95% confidence interval, the alpha value is 0.025, and the corresponding critical value is 1.96. We have included the confidence level and p values for both one-tailed and two-tailed tests to help you find the t value you need.įor normal distributions, like the t distribution and z distribution, the critical value is the same on either side of the mean. For the t distribution, you need to know your degrees of freedom (sample size minus 1).Ĭheck out this set of t tables to find your t statistic. The t distribution follows the same shape as the z distribution, but corrects for small sample sizes.
If you are using a small dataset (n ≤ 30) that is approximately normally distributed, use the t distribution instead.
So if you use an alpha value of p 30) that is approximately normally distributed, you can use the z distribution to find your critical values.įor a z statistic, some of the most common values are shown in this table: Confidence level Your desired confidence level is usually one minus the alpha (α) value you used in your statistical test: For example, if you construct a confidence interval with a 95% confidence level, you are confident that 95 out of 100 times the estimate will fall between the upper and lower values specified by the confidence interval. This is the range of values you expect your estimate to fall between if you redo your test, within a certain level of confidence.Ĭonfidence, in statistics, is another way to describe probability.
#98 confidence interval z score plus
Frequently asked questions about confidence intervalsĪ confidence interval is the mean of your estimate plus and minus the variation in that estimate.Caution when using confidence intervals.Confidence interval for non-normally distributed data.Confidence interval for the mean of normally-distributed data.Calculating a confidence interval: what you need to know.

#98 confidence interval z score tv
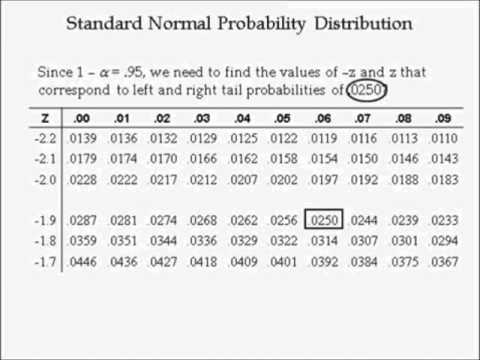
For z*, the sample size is not needed to pick a critical value, but for t*, the critical value changes depending on the sample size. A portion of the z-table is listed below with the part needed for our problem highlighted: Confidence Levelīased on the data, I am 95% confident that the average number of hours teenagers spend each day watching tv is between 3.258 and 3.742 . Note: The critical value was found using a z-table. This is sample statistic you have gotten from your data. Definitions of Key Terms & Other Important Facts Another way to think about it is if we took many samples and created confidence intervals for each one, we would expect the population parameter to lie within approximately 95% of the intervals.įor more information on what these terms mean, proceed below ↓ For example, if we created a 95% confidence interval, we would be 95% confident that the true population parameter was within that calculated interval. This is where confidence intervals come into play. When you make a c onfidence interval, you create a range that can be used to estimate the population parameter.
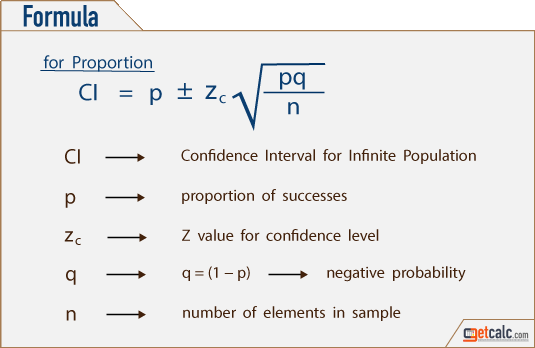
Rather than estimating this parameter with one sample statistic, it might be more helpful to look at the range. Between the two extremes lies the population parameter of 0.5. One person might get 0.55, while another friend might get 0.42, etc. If you and your friends all toss a coin one hundred times, you will probably each get a slightly different proportion of heads.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
